Grayscale images simplify processing by reducing color complexity. A grayscale image contains shades of gray, where each pixel’s intensity ranges from 0 (black) to 255 (white).
OpenCV provides the cv2.cvtColor() function to convert a color image to grayscale.
import cv2
# Read the image
image = cv2.imread('example.jpg') # Load the image in color mode
# Convert to grayscale
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Display the grayscale image
cv2.imshow('Grayscale Image', gray_image)
# Wait for a key press and close the window
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# Optionally save the grayscale image
cv2.imwrite('grayscale_example.jpg', gray_image)
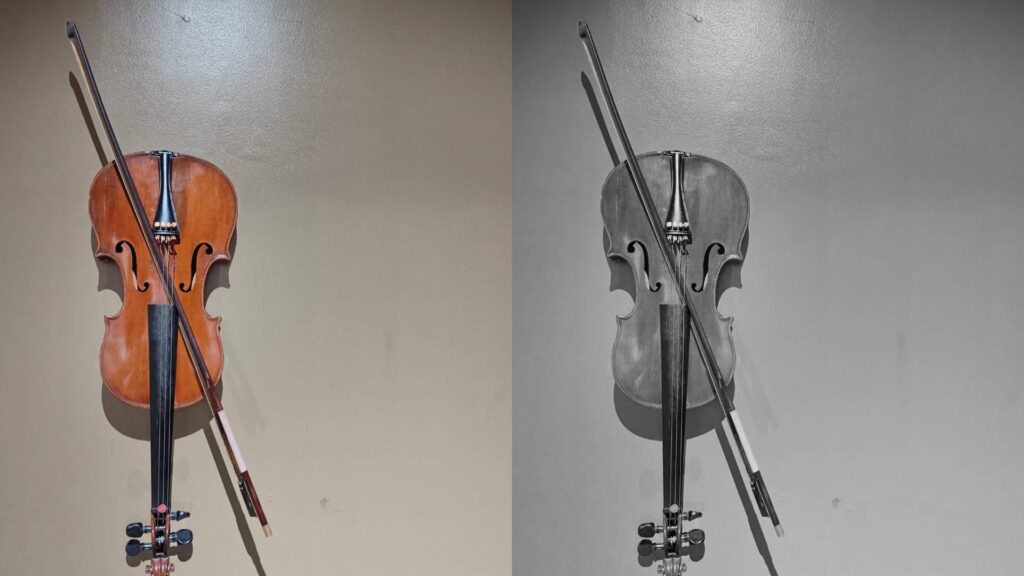

Step 1: Read the Image
image = cv2.imread('example.jpg')- The
cv2.imread()function reads the input image (example.jpg) and loads it in BGR color mode by default.
Step 2: Convert to Grayscale
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)cv2.cvtColor():- Converts the image from one color space to another.
- Arguments:
image: The source image in BGR color format.cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY: Specifies the conversion from BGR to grayscale.
- The output,
gray_image, is a 2D array where each pixel represents the intensity (0-255).
Step 3: Display the Grayscale Image
cv2.imshow('Grayscale Image', gray_image)- Displays the grayscale image in a new window titled
'Grayscale Image'.
Step 4: Wait for Key Press and Close Window
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()cv2.waitKey(0): Waits indefinitely for a key press.cv2.destroyAllWindows(): Closes the display window to free resources.
Step 5: Save the Grayscale Image (Optional)
cv2.imwrite('grayscale_example.jpg', gray_image)
cv2.imwrite():- Saves the grayscale image to a file (
grayscale_example.jpg).
- Saves the grayscale image to a file (
Advantages of Grayscale Conversion
- Simplified Processing: Reduces computational complexity by removing color information.
- Useful for Algorithms: Many image processing algorithms (e.g., edge detection) work on grayscale images.
- Reduced Storage Requirements: Grayscale images consume less memory than color images.
Example Application
This grayscale conversion is often used as a preprocessing step in:
- Face Detection: Simplifies facial feature extraction.
- Medical Imaging: Analyzing X-rays and CT scans.
- Edge Detection: Algorithms like Canny Edge Detection work on grayscale images.
To buy Image Processing books
Digital Image Processing
Image Processing




Good