Resizing an image involves changing its dimensions (width and height) to the desired size. OpenCV provides the cv2.resize() function to perform this operation efficiently.
Syntax:
cv2.resize(src, dsize, fx=0, fy=0, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)Parameters:
src: The input image to resize.dsize: The desired output size (width, height) as a tuple, e.g.,(300, 300). Eitherdsizeor scaling factors (fxandfy) must be provided.fxandfy: Scaling factors for width and height, respectively. Ifdsizeis not provided, these are used to compute the new size.interpolation: Specifies the algorithm used for resizing. Common options:cv2.INTER_NEAREST: Nearest neighbor interpolation (fast but lower quality).cv2.INTER_LINEAR: Bilinear interpolation (default, better quality).cv2.INTER_AREA: Best for reducing size.cv2.INTER_CUBIC: Bicubic interpolation (better quality for enlarging).cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4: High-quality interpolation.
Example Code:
import cv2
# Load the input image
image = cv2.imread('example.jpg')
# Resize the image to 300x300 pixels
resized_image = cv2.resize(image, (300, 300))
# Display the resized image
cv2.imshow('Resized Image', resized_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()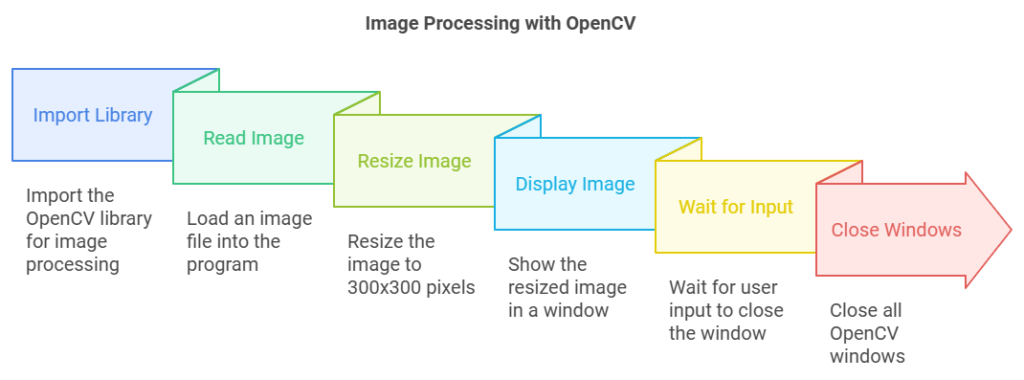
How Resizing Works:
- The original image’s dimensions are adjusted to the specified size
(300, 300)in this case. - The interpolation method determines how pixel values are calculated during resizing:
- For enlarging, algorithms like
INTER_CUBICorINTER_LANCZOS4produce smoother results. - For reducing,
INTER_AREAminimizes distortion.
- For enlarging, algorithms like
Scaling with fx and fy:
Instead of providing exact dimensions, scaling factors can be used:
# Scale the image to half its size
scaled_image = cv2.resize(image, None, fx=0.5, fy=0.5, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)Here:
fx=0.5scales the width to 50% of the original.fy=0.5scales the height to 50% of the original.
Common Use Cases:
- Standardizing Image Size: For machine learning models, where uniform input size is required.
- Thumbnail Generation: Reducing image size for previews or web usage.
- Improving Processing Speed: Smaller images require less computational power.
Key Notes:
- Aspect Ratio: To preserve the original aspect ratio, calculate dimensions manually or use scaling factors (
fxandfy). - Performance: For enlarging, use smoother interpolation methods like
INTER_CUBICfor better quality. For reducing,INTER_AREAis more efficient.
This flexibility makes cv2.resize() a vital tool in image processing!
To buy Image Processing books
Digital Image Processing
Image Processing



